We focus on financial statement reporting and do not discuss how that differs from income tax reporting. Therefore, you should always consult with accounting and tax professionals for assistance with your specific circumstances. Such bonds were known as bearer bonds and the bonds had coupons attached that the bearer would “clip” and deposit at the bearer’s bank. The bond’s total present value of $96,149 is approximately the bond’s market value and issue price. Market interest rates are likely to increase when bond investors believe that inflation will occur. As a result, bond investors will demand to earn higher interest rates.
Cost Basis

This is the simplest way to amortize a bond, but it is not recognized by the IRS for tax purposes. As an investor, it is crucial to understand how amortized bonds work because the interest paid back counts as income for you. Amortized bonds are loans in which the borrower pays back both the principal and the interest throughout the life of the loan.

Jayster Company issued bonds at a discount. The semi-annual journal entry for interest expense will include:
Callable bonds are bonds that give the issuing corporation the right to repurchase its bonds by paying the bondholders the bonds’ face amount plus an additional amount known as the call premium. A bond’s call price and other conditions can be found in a bond’s contract known as the indenture. The difference between the 10 future payments of $4,500 each and the present value of $36,500 equals $8,500 ($45,000 minus $36,500). This $8,500 return on an investment of $36,500 gives the investor an 8% annual return Legal E-Billing compounded semiannually.
Bonds Payable Issued at a Discount
By amortizing the bonds, you avoid paying taxes on the interest income all at once and instead spread it out over the life of the bond. A bond premium occurs when the price of the bond has increased in the secondary market due to a drop in market interest rates. A bond sold at a premium to par has a market price that is above the face value amount. The bond amortization calculator calculates the bond issue price, which is a function of both the bond rate and the market rate. Below is a comparison of the amount of interest expense reported under the effective interest rate method and the straight-line method. Note that under the effective interest rate method the interest expense for each year is decreasing as the book value of the bond decreases.
- One of the topics that often comes up when discussing bond premium is its advantages and disadvantages.
- This means that when a bond’s book value decreases, the amount of interest expense will decrease.
- The existing bond’s semiannual interest of $4,500 is $500 less than the interest required from a new bond.
- But the bond premium has to be amortized for each period, and a reduction of cost basis in the bond is necessary each year.
- Recall that this calculation determines the present value of the stream of interest payments only.
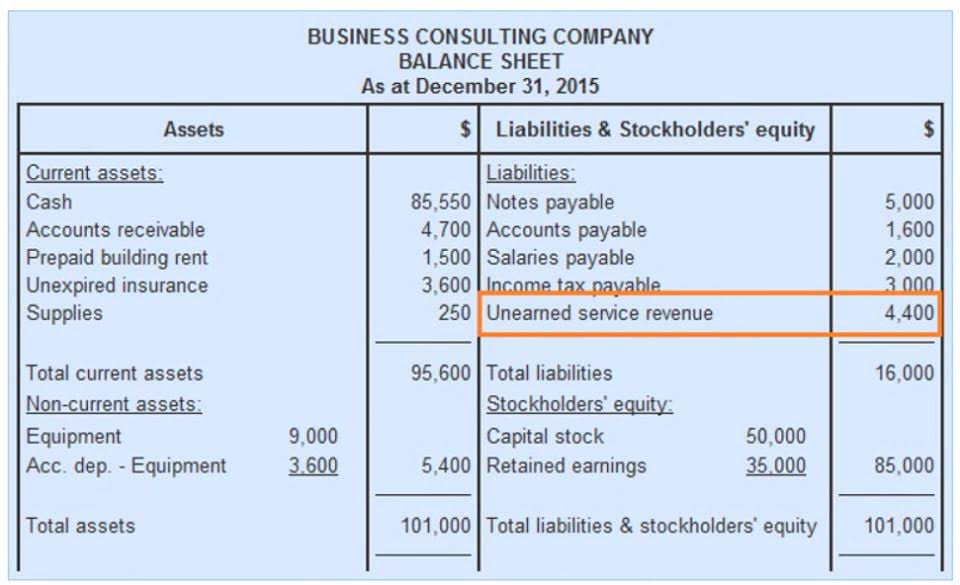
Things that are resources owned by a company and which have future economic value that can be measured and can be expressed in dollars. Examples include cash, investments, accounts receivable, inventory, supplies, land, buildings, equipment, and vehicles. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31. The balance sheet is also referred to as the Statement of Financial Position. Bonds allow corporations to use financial leverage or to trade on equity.
It influences the present value of the bond and the calculation of interest and principal payments. These examples illustrate the accounting procedures used for discounts. Premiums are handled in a similar manner except that the premium decreases interest revenue and is recorded by crediting the Investment in Bonds account.

Bonds have a lower cost than common stock because of the bond’s formal contract to pay the interest and principal payments to the bondholders and to adhere to other conditions. A second reason for bonds having a lower cost is that the bond interest paid by the issuing corporation is deductible on its U.S. income tax return, whereas dividends are not tax deductible. Investors should consider the tax implications of their bond investments when developing a wealth management strategy. By selecting bonds with favorable tax treatment, such as municipal bonds, and managing bond premium amortization, investors can optimize their portfolios for tax efficiency. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows investors to deduct the annual amortization of recording transactions bond premiums from their taxable income.
- It influences the present value of the bond and the calculation of interest and principal payments.
- We will use present value tables with factors rounded to three decimal places and will round some dollar amounts to the nearest dollar.
- This process ensures that the bond’s book value approaches its face value by maturity, providing a more accurate representation of the company’s financial obligations.
- In practice, if there are material differences between the two methods, the effective interest method should be used.
- When a bond is amortized, the principal amount, also known as the face value, and the interest due are gradually paid down until the bond reaches maturity.
- Typically, the calculations are done in such a way that each amortized bond payment is the same amount.
Amortizing Bond Discount with the Effective Interest Rate Method

A bond is sold at a discount when its coupon rate is lower than the bond premium amortization schedule market rate. Investors pay less than the bond’s face value because its interest payments are less attractive. The discount is gradually amortized, meaning it is added back to the bond’s carrying value over time.
Day Count Methodology
The preferred method for amortizing the bond premium is the effective interest rate method or the effective interest method. Under the effective interest rate method the amount of interest expense in a given year will correlate with the amount of the bond’s book value. This means that when a bond’s book value decreases, the amount of interest expense will decrease. In short, the effective interest rate method is more logical than the straight-line method of amortizing bond premium.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.